Ho Chi Minh City has officially introduced its New Generation International Financial Center (IFC Vietnam), marking a transformative step toward becoming a global financial hub. With large-scale planning, strong incentives, and a hybrid legal system, the IFC targets global institutions, foreign investors, and top talent.

Contents
Vietnam’s aspiration to establish itself as a new destination on the global financial map is taking shape following the National Assembly’s adoption of Resolution No. 222/2025/QH15 on an International Financial Centre (IFC). From December 2025, HCMC will launch its New Generation IFC, set to become a major hub for global capital flows. The HCMC International Financial Center spans 898.7 hectares across District 1 and Thu Thiem.
At its core lies a 9.2-ha central zone designated for management and regulatory bodies. The masterplan features 11 functional zones, including banking clusters, fintech districts, digital trading floors, and financial service towers. Furthermore, a major highlight is the 99-storey International Operations Tower, supported by 40–50-storey towers for global investment institutions. Due to national security requirements, this iconic 99-storey tower will be developed exclusively by Vietnamese companies.

Not only the 99-storey tower planned for construction, the main symbol of this new IFC area cannot fail to mention Saigon Marina IFC. This is the first office tower in Vietnam to be developed according to the TOD (Transit Oriented Development) orientation, with an underground passage directly connecting Ba Son Metro Station – Metro Line 1. Along with the connection, Saigon Marina IFC is achieves an international standard building for sustainability when achieving LEED Gold certification from the US Green Building Council (USGBC). Its commitment to sustainable development and social responsibility to partners and customers.

According to the orientation when establishing, the IFC HCMC is designed to operate as a multi-functional global finance hub. From that, its offering diverse financial services such as:

These functions help this new area of Ho Chi Minh City become an attractive financial destination for foreigners. It is corresponding to the models of Singapore or some Southeast Asian countries in particular and of the Asian region in general.
To attract high-value investors, the IFC provides one of the most competitive tax packages in the region. According to Resolution 222/2025/QH15 of the National Assembly, the outstanding competitive advantages of this region include:
Compared to the Singapore IFC region, which applies a corporate income tax of 17% and a progressive personal income tax of 0%-24%, IFC Vietnam has quite a few incentives. Vietnam offers competitive costs, with financial services, office rents and talent expenses far lower than in Singapore and Hong Kong.

These relaxed IFC policies in Vietnam, especially in HCMC, create strong opportunities for businesses to participate early. More flexible mechanisms in IFC contribute to providing more incentives to attract foreign companies and capital to Vietnam.
A key appeal of HCMC’s new IFC is its first-ever use of Common Law in Vietnam. Under this model, legal precedents and court rulings become a valid source of law, creating a predictable, transparent, and internationally familiar legal environment for financial institutions.
Common Law, originating from the UK and widely adopted in major global financial hubs such as London, Singapore, and Hong Kong, which is particularly suited for fast-changing sectors like fintech, digital assets, and cross-border investment. This system lets foreign investors operate confidently, reducing local-law uncertainty and strengthening commercial security and deal reliability.
Outside the IFC zone, Vietnamese law continues to apply. To ensure fairness and transparency, the center is governed by three independent authorities:
This multi-layer governance improves oversight and boosts investor trust through transparent operations, credible enforcement, and reliable dispute resolution. These are all essential factors for high-value international financial activities.
As a financial center, the factor of capital flow rules in transactions is of concern for many investors. In the future, capital movement in the IFC will be fully liberalized with clear rules.
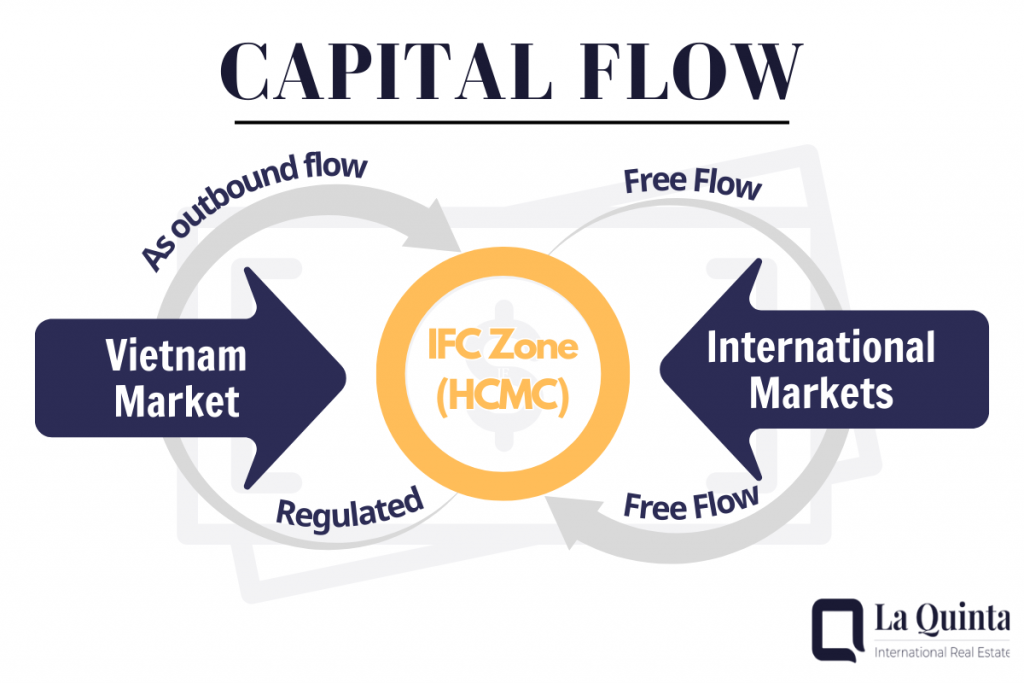
Currently, Vietnamese individuals cannot invest directly in the IFC; only qualified domestic institutional members are permitted. Authorities are also currently considering the introduction of future investment quotas for individuals and signaling potential expansion of participation.
The development of the IFC will follow a three-phase roadmap designed to elevate Ho Chi Minh City into a leading financial hub in Asia. Roadmap are include in:

With strong planning, global-standard incentives, and transparent governance, IFC Vietnam is poised to elevate HCMC into an emerging Asian financial hub. For investors, this signifies long-term opportunities in a rapidly developing, strategically located financial ecosystem. This is an important time to open up long-term opportunities for investors in a rapidly developing financial ecosystem. Long-term financial investment opportunities such as fin-tech or real estate assets will bring stronger investment and transaction values to investors.
With a mission to support international investors in Vietnam, La Quinta provides full market insights, forecasts, and legal updates to help investors make informed, effective decisions in this fast-growing market.
More potential real estate in the IFC HCMC area
